PCB Board Manufacturers USA
Application and Use of PCBs
Most electronic equipment has at least one PCB or Printed Circuit Board as their key component. Although most users of such equipment are unaware of the existence of a PCB within, the board is critical not only to its proper functioning, but also to the existence of the industry manufacturing such equipment. While applications of a PCB may range to massive numbers, it is easier to group these applications industry-wise. But first, we must look at the necessity of a printed circuit board.
Why Use a PCB?
An instrument or equipment contains many electronic components that help in achieving its intended functioning and performance. A printed circuit board allows a convenient method of electrically interconnecting these electronic components while providing a mechanical structure for holding them together in a safe manner. Without using a PCB, it would be almost impossible for an Original Equipment Manufacturer or OEM to physically interconnect hundreds of electronic components that a gadget may contain, and then reproduce this arrangement for any number of units they are likely to produce.

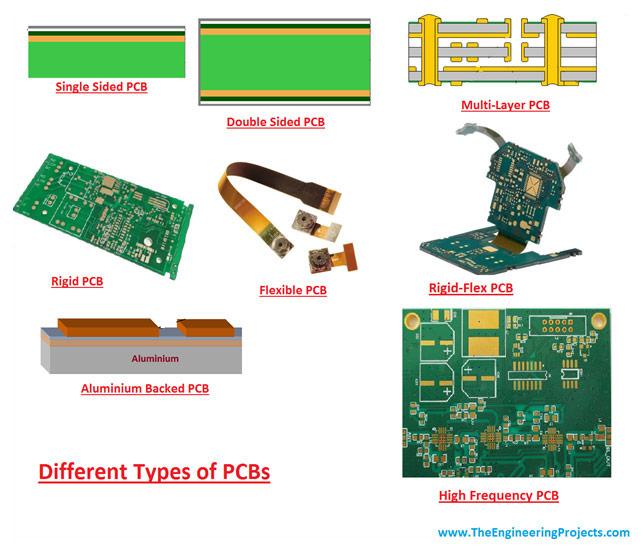
Types of PCBs
The use of a PCB defines its type. While a simple FR-4 grade PCB will suffice for most standard applications, a more demanding performance calls for specially developed PCBs. For instance, while an FR-4 board is adequate for a simple LED light, a high-power LED light must use a metal-clad PCB, and a wearable sports device requires a flexible PCB. Likewise, for fabricating a sophisticated computer motherboard, the manufacturer must use HDI or High-Density Interconnect technology.
Irrespective of the type, the base of any PCB is a non-conductive material with copper traces and pads on it, forming interconnections between the several electronic components soldered onto the pads. Depending on the complexity of the circuit, a PCB may be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered. While a single-sided board has copper traces and pads on only one of its sides, the double-sided board has them on both its sides, and several single-sided boards sandwiched together make up a multi-layered board.
Industry-Wise Application of PCBs
Most common applications of PCBs according to the industries that use them are:
- Medical and Healthcare Industry
- Illumination and Lighting Industry
- Consumer Electronics Industry
- Industrial Equipment Industry
- Aerospace Industry
- Maritime Industry
- Automotive Industry
- Safety and Security Equipment Industry
- Telecommunications Industry
- Military and Defense
Medical and Healthcare Industry
With the advancement of technology and capabilities, the medical and healthcare industry is increasingly using electronic equipment they use for treatment, monitoring, diagnostics, and more. PCBs meant for equipment in the medical and healthcare industry require special attention for ensuring reliability, as the proper functioning of medical equipment is crucial to the health of patients. Equipment meant for implantation into the human body must meet strict standards for sanitation. The medical and healthcare industry uses PCBs in several devices, including pacemakers, infusion pumps, monitors, imaging systems, and more.
Illumination and Lighting Industry
The illumination and lighting industry favor Light Emitting Diodes or LEDs because of their long life, energy efficiency, and compactness. These advantages also make LEDs the most popular lighting technology across numerous industrial, commercial, and residential establishments.
PCBs in the illumination and lighting industry have a dual role to play. One of them is to provide a mechanical base for mounting the LEDs while connecting them electrically. The second role is to remove the heat from the LEDs, which they generate while operating—operating LEDs in high temperature reduces their average life.
High power LED lights, therefore, use aluminum backed PCBs. The metal transfers the heat away from the LEDs, eliminating the need for an additional heat sink, thereby allowing the luminaire to remain compact. The illumination and lighting industry use LED PCBs in several devices, including medical lighting, computer displays, automotive displays, display lighting, street lighting, and more.
Consumer Electronics Industry
Commonly used electronic products in homes and offices, such as computers, smartphones, printers, radios, televisions, telephones, and more, require a PCB to function. Manufacturers produce PCBs for the consumer electronics industry in high volumes and at low cost, as the segment is price-conscious. However, the reliability of these PCBs must be high, as businesses expect to stay in business. Consumer devices that use PCBs include home appliances, communication devices, personal computers, entertainment systems, and more.
Industrial Equipment Industry
The industrial equipment industry uses a huge quantity of PCBs annually, as most of their equipment are electronically controlled. This includes equipment in use in manufacturing, distribution, and other facilities.
PCBs for Industrial equipment must be robust enough to withstand the harsh environments typical of industrial facilities. Industrial equipment often has to handle harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures, vibrations, and/or rough handling. Therefore, manufacturers often build industrial PCBs using more durable material than they use for conventional types. Industrial PCBs may be thicker and made of a material that exhibits a greater tolerance to thermal excursions. The industrial equipments that uses PCBs includes measuring equipment, power equipment, testing equipment, robotics, IIoT, and control equipment, and manufacturing equipment.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry uses special PCBs as the equipment in this industry often face incredibly harsh conditions. Aerospace equipment uses PCBs extensively for their communication, monitoring, power supply, and distribution applications in radio communication systems, satellites, space shuttles, and airplanes. PCBs for the aerospace industry needs to be extremely robust and highly dependable, as they may have to perform in outer space, where replacing a defective board may not be possible.
Maritime Industry
All types of navigation equipment, communication systems, submarines, large cargo ships, and small marine vessels extensively use electronic equipment and hence contain innumerable numbers of PCBs. Exposure to freshwater, saltwater, and water vapor corrodes electronic components and PCB materials easily. Therefore, PCBs and components the maritime industry uses have durable material as their base and undergo a special treatment to prevent them from succumbing to corrosion. The naval industry uses PCBs in the equipment they use for control and navigation of ships.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is increasingly using PCBs in their vehicles to make driving safer and easier, and for providing numerous advanced features. The presence of vibration and extreme temperatures inside a vehicle demands that PCBs used must be able to withstand these conditions and continue to perform without failure. The automotive industry uses PCBs mostly for mounting sensors for control systems, engine management, fuel regulation, navigation, and in-car entertainment systems.
Safety and Security Equipment Industry
Advancements in electronic components have resulted in the presence of a wide variety of safety and security equipment in the market. These include fire and intruder alarms, motion sensors, electronic locks, smoke and gas detectors, security cameras, and many more. PCBs play an essential role in all the above equipment, and more so as most security equipment nowadays connects to the internet for remote access.
Telecommunications Industry
The telecommunications industry uses PCBs in almost all its equipment, starting from displays and indicators to communication equipment for home and office use and outdoor equipment such as communication towers. PCBs in this equipment may have to withstand extreme temperatures, thunderstorms, ice, and snow.
Military and Defense
PCBs for military and defense equipment covers a vast range of applications. As they are often necessary for national defense, the equipment and PCBs therein need to be exceptionally durable and reliable. Military and defense use such PCBs in their vehicles, firearms, computers, communication, and monitoring equipment.
As military and defense operations may cover different geographical locations, their equipment and PCBs must withstand extreme temperature and weather conditions.
Conclusion
Printed circuit boards are now an unavoidable part of our lives. Most electronic equipment we use daily, such as computers, smartphones, refrigerators, air-conditioners, vehicles, entertainment systems, and more, have a printed circuit board inside that allows it to function and perform to our satisfaction.
Read More